SLF4J vs log4j vs logback vs log4j2
https://stackify.com/compare-java-logging-frameworks/
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/slf4j/slf4j_vs_log4j.htm
SLF4J
SLF4J (Simple Logging Facade for Java) is not an implementation of logging framework, it is an abstraction for all those logging frameworks
以后写程序都用这个,相当于定义了接口,需要什么实现(log4j log4j2 logback等)只需要引入相应的包即可,而不需要修改代码。
public class MyClass {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass().getName());
public void myMethod() {
log.info("This is an info message");
// ...
}
}The architecture of SLF4J takes advantage of the Java Service Loader mechanism: it allows it to work with abstractions, and to use the implementation provided at runtime on the classpath.
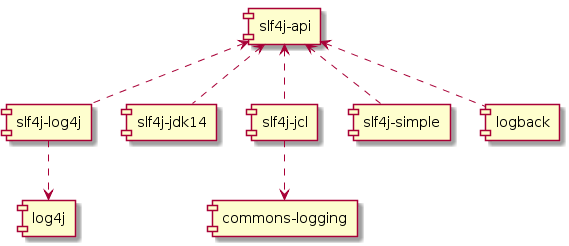
In essence, at compile-time, use SLF4J API, and any desired library at runtime. Out-of-the-box libraries include:
JAR
DESCRIPTION
slf4j-log4j
Redirects calls from SLF4J to Log4J
slf4j-jdk14
Redirects calls from SLF4J to JUL
slf4j-jcl
Redirects calls from SLF4J to Java Commons Logging
slf4j-simple
Write logs to the console
slf4j-logback
Uses the Logback library
BridgesTo allow an easy migration path from any of the previous logging frameworks (Log4J, JUL, or Commons Logging), SLF4J offers bridges to redirect calls from one of them to SLF4J:
JAR
DESCRIPTION
jcl-over-slf4j
Redirects calls from Commons Logging to SLF4J
log4j-over-slf4j
Redirects calls from Log4J to SLF4J
jul-over-slf4j
Redirects calls from JUL to SLF4J
Probably because of those bridges, SLF4J became very popular, even more so than Log4J… in some cases, SLF4J used as an API, while Log4J used as an implementation.
log4j
很老了,2015年停止维护了,只有老项目在用。(项目里应该配置了 log4j.properties 文件)
不能原生支持SLF4J,需要引入额外包:
Log4j doesn’t support SLF4J natively. You also need to add the following dependency to be able to use Log4j via the standardized interfaces.
Logback
Logback was written by the same developer who implemented Log4j with the goal to become its successor。
默认不需要配置文件:Logback doesn’t require any configuration. By default, it writes all log messages in DEBUG level or higher to standard out. You can change that with a custom configuration file in XML or Groovy format.
Spring Boot 默认使用Logback。引入 Spring Boot 什么都不改即用Logback。
Log4j2
Log4j2 packages its API and implementation in two separate jar files. You can implement and build your application using the log4j-api.jar, and you need to provide the additional log4j-core.jar at runtime. If you want to use the SLF4JAPI, you also need the log4j-slf4j-impl.jar file, which contains a bridge between the two APIs.
Log4j2 本身包含两部分,自己定义的 API 和该 API 的实现,可以只引入 API 然后自己实现。如果需要使用 Log4j2 作为 SLF4J 的实现,需要在两种 API 之间进行桥接,即引入 log4j-slf4j-impl.jar。
如果要在 Spring Boot 中使用 Log4j2:
配置 log4j2.xml:
一些奇怪的转换
Difference between log4j-to-slf4j and log4j-over-slf4j
Difference between slf4j-log4j12 and log4j-over-slf4j
Apache Commons Logging
Difference between Simple Logging Facade for Java and Apache Commons Logging
What is the issue with the runtime discovery algorithm of Apache Commons Logging
Apache Commons Logging (previously known as Jakarta Commons Logging or JCL)
JUL java.util.logging
Last updated